- AyurVAID Pharmacy
Eczema, or “Vicharchika” in Ayurveda, is an umbrella term for a group of skin conditions marked by inflammation, itching, dryness, and recurrent flare-ups. It affects people of all ages and tends to appear on hands, elbows, the face, and the scalp. The symptoms frequently fluctuate and have a significant impact on sleep, mental health, and overall quality of life.
In modern medicine, eczema includes a spectrum of skin conditions—like atopic dermatitis and contact eczema—and is usually managed with steroids or antihistamines. However, these treatments often offer only temporary relief, accompanied by a risk of side effects and a higher likelihood of recurrence.
Ayurveda recognises Vicharchika as a Tridoshaja Kushtha, predominantly involving Kapha and Pitta doshas, with Vata playing a role in dryness and cracking. Aggravated doshas, caused by factors like improper diet, poor digestion, stress, and environmental triggers, lead to the manifestation of skin lesions and intense itching. All skin disorders result from the involvement of three doshas, along with twak (skin), rakta (blood), mamsa (muscle tissues), and lasika (lymphatic system).
In Apollo AyurVAID, eczema management is a comprehensive, widely individualised, and protocol-driven approach (Precision Ayurveda). The approach aims to tackle the root causes of the disease rather than manage its symptoms.
The whole-person health assessment identifies the condition’s root cause. Following such an assessment, a trained team of Ayurveda physicians designs a personalised protocol combining classical Ayurveda medications and therapies, detoxification of a specific nature, and changes in diet and lifestyle.
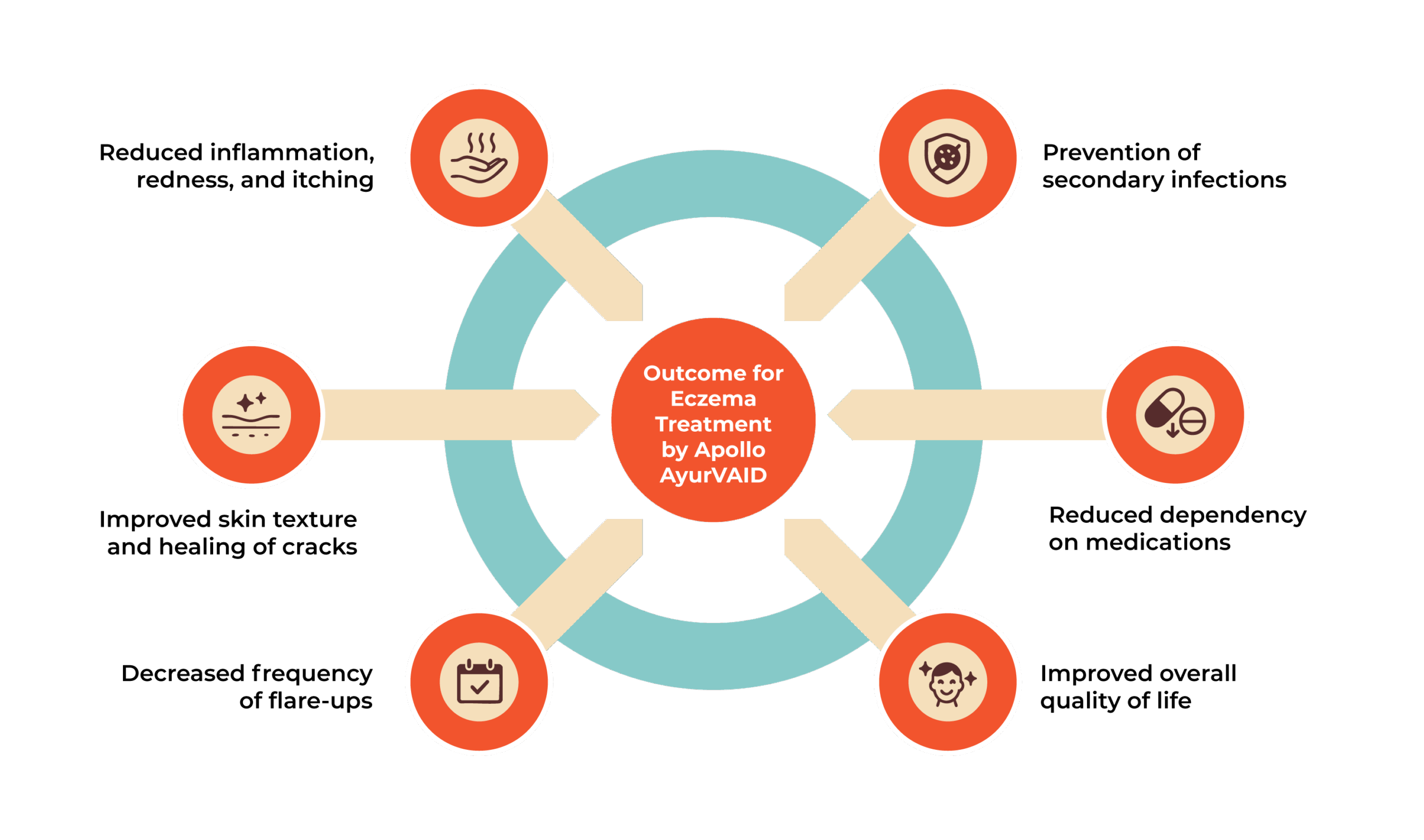
Our treatment aims to reduce inflammation, restore skin barrier function, and prevent flare-ups, offering long-term relief and improved quality of life without steroid dependence.
Modern medicine describes eczema as a chronic inflammatory skin condition with deeper systemic imbalances involving immunity, skin barrier dysfunction, environmental triggers, and genetic susceptibility.
The treatments are aimed at symptom control and inflammation management. These are
Ayurveda treatment for eczema is comprehensive. The patient can expect the following services along with conventional treatment:
The disease originates from complicated interactions between the physiological imbalances of Kapha, Pitta, and Vata doshas. Different dietary, lifestyle, and environmental factors cause these imbalances in different individuals. The following list includes some of these contributing factors:
Dietary Factors (Aharaja):
Lifestyle Factors (Viharaja):
Psychological Factors (Manasika):
Physiological Changes:
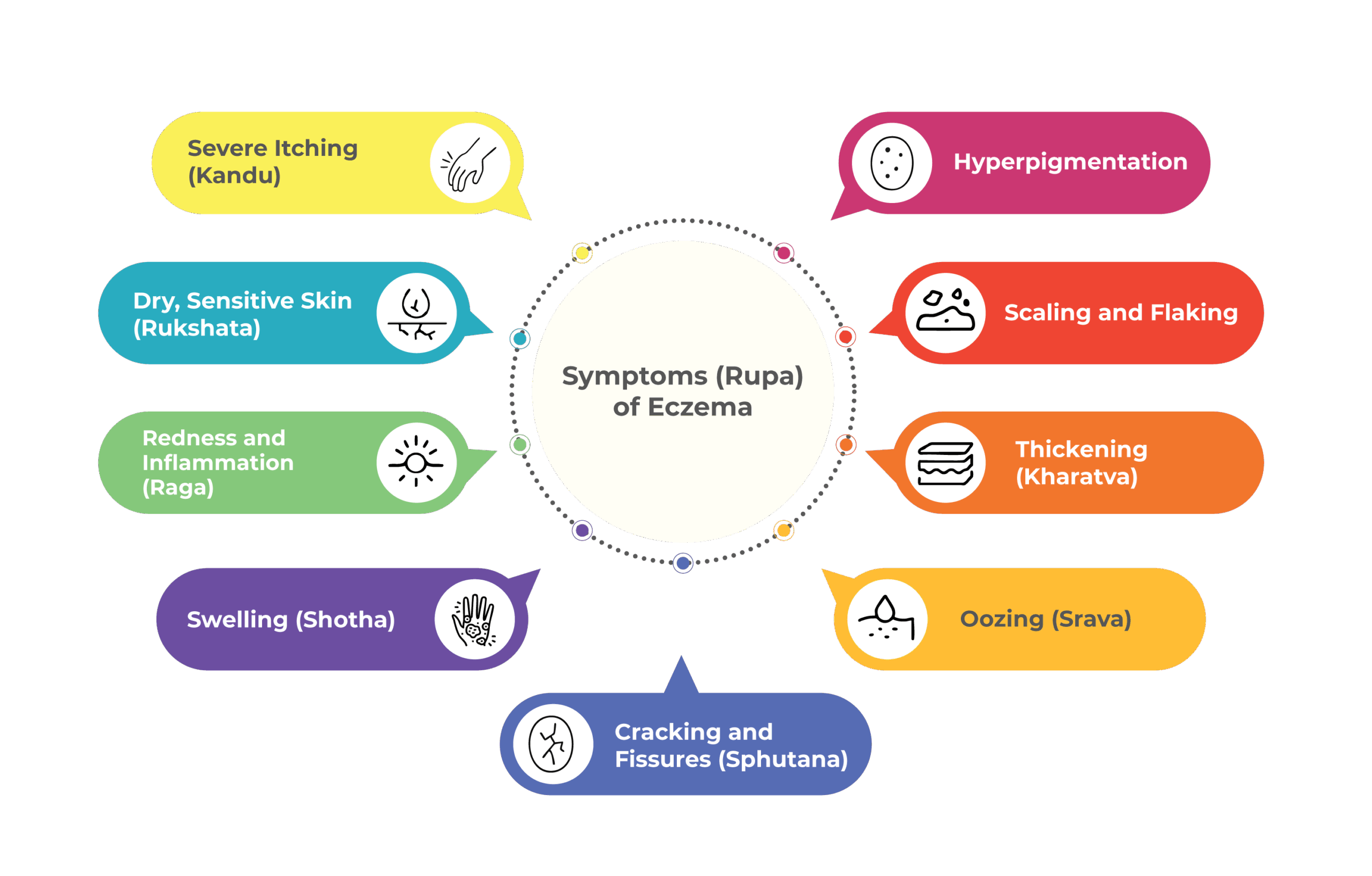
Eczema appears with several signs and symptoms, such as
Tridosha Imbalance (Dosha Prakopa)
The evolution of eczema starts with the vitiation or derangement of the three basic doshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. Each dosha produces the condition differently: Vata causes dryness, roughness, and cracking of the skin; Pitta produces inflammation, redness, and burning; and Kapha causes oozing, swelling, and pruritus. Depending on the leading dosha, the clinical picture of eczema differs, thus rendering the condition multifaceted in its presentation.
Compromised Digestion and Toxin Production (Agni Mandya and Ama Utpatti)
When Agni (digestive fire) is low, it causes improper digestion of food, which in turn creates metabolic toxins called Ama. These toxins get absorbed in the system and flow through the Rasa (lymph system) and Rakta (blood), resulting in skin deposition. This deposition irritates the tissues, causes inflammation and an immune response, and contributes to long-term conditions such as eczema.
Blockage of Channels of Nutrition (Srotorodha)
The Ama collection clogs the Rasavaha and Raktavaha Srotas, i.e., the highways for transporting nutrition to the skin. The clog disturbs normal nourishment and cleansing of the tissues, resulting in the engorgement of waste and a dosha imbalance. The skin is deprived of the necessary nutrients, which leads to the development of lesions, discoloration, and other pathological alterations.
Skin Barrier Dysfunction
As doshas build up and channels get clogged, the body’s natural defence barrier in the skin gets disrupted. In healthy skin, the skin keeps moisture inside and prevents environmental irritants and allergens from reaching the skin. In eczema, the defence barrier weakens, leading to enhanced loss of moisture and entry of external irritants into the skin, which, in turn, further exacerbates the skin and continues the inflammatory process.
Immune Dysregulation and Disturbance of Ojas
With chronic doshic imbalance and toxin buildup, the immune resilience of the body, as symbolised by Ojas, gets disrupted. Ojas is the one that keeps immunity, tissue resilience, and resistance to illness intact. When compromised, it leads to dysregulation of the immune system, manifesting as an excess of skin hypersensitivity, allergic dermatitis, and persistent inflammation—characteristics of eczema from an Ayurveda point of view.
Pathogenesis into Chronicity
When not treated or if poorly treated, eczema becomes chronic. Vata dosha gains prominence, and the skin becomes drier; the thickness of the skin (lichenification) increases, cracks become deep, and chronic flaking occurs. Chronic conditions are more difficult to treat and need deeper systemic purgation and long-term rejuvenation treatments in Ayurveda.
Dosha-Specific Clinical PresentationsEczema may occur in various clinical patterns depending on the dominant dosha. In Pitta-Kapha predominant types, the condition is marked by redness, heat, oozing, and inflammation and is amenable to cooling and drying therapy. In contrast, eczema that is mainly Vata-Kapha shows dryness, flaking, and cracks, and is treated with therapies that nourish, lubricate, and moisturise to fix the imbalance and promote healing.
Our specially trained doctors carry out this assessment, which looks closely at your current health issues, medical history, possible causes (Nidana Panchaka), and how the disease develops using clinical methods like Ashta Sthana Pariksha (an 8-part exam), Dasha Vidha Pariksha (10 factors), and Srota Pariksha. Relevant blood tests (complete blood count with eosinophil count and IgE levels) and dermatological assessments (EASI score and SCORAD index) are used for complete evaluation. Relevant blood tests (complete blood count with eosinophil count and IgE levels) and dermatological assessments (EASI score and SCORAD index) are used for complete evaluation.
A comprehensive disease tree, from root cause to all signs and symptoms, is derived from causative factors, imbalance in doshas, involved subsystems, and progression. This traces the individual course of disease for each person.
Based on the disease tree and assessment, we create a customised treatment plan that aims to improve skin health, reduce inflammation, and effectively reverse the disease process.
The plan includes classical Ayurveda medication, therapies, and targeted detoxification procedures, complemented by personal diet and lifestyle adjustments, which fall under the natural eczema treatment protocol. It tracks all dermatological and health parameters to focus on skin healing and reducing inflammation.
Standardized scales, such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD), and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), help monitor skin lesions, disease progression, and impact on quality of life.
The Apollo AyurVAID’s protocol-driven approach (Precision Ayurveda) focuses on controlling symptoms and aims to prevent disease progression, minimise discomfort, and enhance the quality of life.
Ayurveda treatment for eczema takes a holistic approach. It aims to balance the doshas, eliminate toxins, restore healthy skin function, and improve overall vitality. The type of atopic eczema – Ayurveda treatment, and its duration are tailored to the severity of the disease.
Reducing Inflammation/Itching (Poorvakarma Stage):
Objective: The Poorvakarma stage prepares the body for treatment by establishing digestive balance and beginning the detoxification process. It treats acute symptoms such as itching and inflammation, decreases metabolic toxins (Ama), and enhances digestive fire (Agni).
Duration: ~ 7-10 days
Internal Medications: These are administered according to the dosha imbalance to enhance the Agni, support digestion, and eliminate Ama, resulting in quick relief from itching and inflammation.
External Therapies: Lepa (herbal paste application), Parisheka (pouring of medicated decoctions), and Abhyanga (oil therapy) are applied to reduce local inflammation, lubricate dry skin, and soothe itching.
Reversing the pathogenesis: Panchakarma Therapies
Objective:Panchakarma aims to cleanse the body, remove toxin accumulation in channels and tissues, and balance doshas.
Duration: ~ 14-21 days
For Predominant Pitta-Kapha Imbalance:
For Predominant Vata-Kapha Imbalance:
External Therapies: Therapies such as Abhyanga (oil therapy), Kashaya Dhara (herbal decoction bath), and Lepana (application of medicated pastes) are performed for both patient types to improve skin health and reduce symptoms.
Diet: Cool, anti-inflammatory foods for Pitta-type; light, warming, and moisturising foods for Vata-type.
Nourishing and External Therapies
Duration: 3-6 months
Rasayana Therapy: Rejuvenative medicines and blood purifiers to enhance immunity, improve skin health, and prevent recurrence are prescribed.
External Applications: Regular application of medicated oils (taila) and medicated ghee preparations for continuous skin nourishment and barrier repair.
Lifestyle Modifications: This includes dietary changes such as avoiding trigger foods, practicing stress management techniques, engaging in yoga and mild exercise, and following seasonal regimens (Ritucharya) to maintain skin health and prevent flare-ups. These practices can be performed at home or on an OP basis.
For severe or chronic eczema, the above strategy is adapted for maintenance and retarding the exacerbation, with more aggressive treatment during flare-ups.
NOTE: The length of the treatment can vary based on the disease’s chronicity, severity, involved body surface area, and comorbidities.
AyurVAID follows a structured, protocol-driven approach to ensure effective treatment and sustainable recovery.
To ensure effective treatment and track progress, baseline values are taken using:
Case 1:
A 51-year-old male patient suffering from chronic eczema
Case Summary: The patient presented with complaints of dry, scaly, itchy skin rashes with the occasional oozing of blood upon scratching. The lesions were distributed over the lower back. The symptoms affected his legs, thighs, abdomen, elbows, and scalp. He had been experiencing these symptoms for 8 years, with significant aggravation over the past 6 months. The condition worsened during winter. Additionally, he had associated symptoms of chronic nasal obstruction for 6 years.
He underwent a 35-day Ayurveda treatment course at Apollo AyurVAID, which included Sarvanga Utsadana with Bashpa Sweda, Sthanika Utsadana, Pratimarsha Nasyam, Sthanika Kashayadhara, Sarvanga Abhyanga with Bashpa Sweda, Virechana, and Nasya, along with internal medications and external applications.
At baseline, he had a PASI score of 30.4 and a DLQI score of 18, indicating severe skin involvement and a very large impact on quality of life. At the end of the treatment, the PASI score reduced to 26.4, and DLQI improved to 11, indicating a shift to a moderate impact on quality of life. Clinically, there was a marked reduction in scaliness, induration, itching, and oozing. Overall vitality improved, stress levels decreased (scale from 4/5 to 2/5), and well-being improved from low to moderate.
At discharge, he was prescribed maintenance medications and advised dietary and lifestyle modifications to sustain improvement and prevent relapse. A follow-up was scheduled after 15 days.
Case 2:
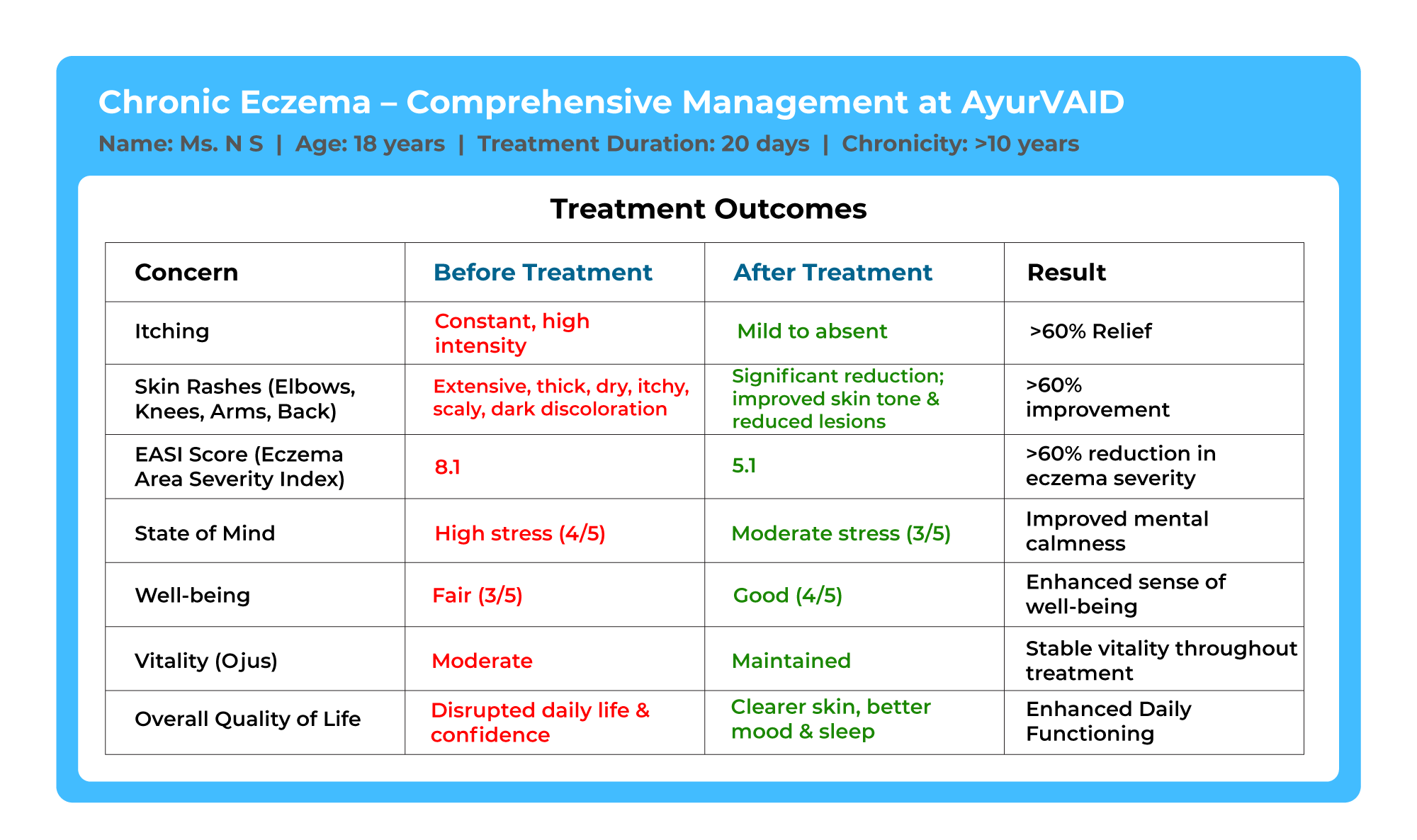
An 18-year-old female patient complained of chronic eczema
Case Summary:
An 18-year-old student had been suffering from chronic eczema (vicharchika) for over 10 years, with worsening symptoms over the past 2 years. She presented with thickened, itchy, dry, and scaly skin along with dark discoloration over the elbows, knees, arms, and back. Spicy and non-vegetarian food aggravated her symptoms. Previous allopathic and homeopathic treatments provided only temporary relief. She also experienced fatigue for the last three months.
She underwent a 21-day inpatient Ayurveda treatment at Apollo AyurVAID Hospitals, which included Thailalepanam, Lepam, Snehapana, Kashayadhara, Abhyanga with Bashpasweda, Virechana, and Takradhara.
Post-treatment, her EASI score improved from 8.1 to 5.1, with approximately a 60% reduction in itching and scaling. Clinical signs such as skin thickness, discoloration, and dryness also reduced significantly. Fatigue resolved, stress levels reduced (4 to 3), and well-being improved (3 to 4).
She was discharged with advice on diet, lifestyle, and follow-up care after two weeks, with recommendations for long-term management.
“I had been struggling with eczema that kept recurring despite allopathic treatment, but after 21 days of therapy at AyurVAID, my condition significantly improved and I feel much better. The treatment, care, and support from the doctors, nurses, and entire staff were exceptional—everything from the systematic diet to timely attention made the healing experience truly remarkable.”
Ms RR, 27 years
As we work hard to improve our services, your feedback is important to us. Please take a moment to help us serve you better.
The information provided in this blog is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician, Ayurvedic practitioner, or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.
Subscribe to our hospital newsletter for the latest health tips, updates on services, patient stories, and community events. Sign up today and stay informed!







Popular Searches: DiseasesTreatmentsDoctorsHospitalsWhole person careRefer a patientInsurance