FAQs
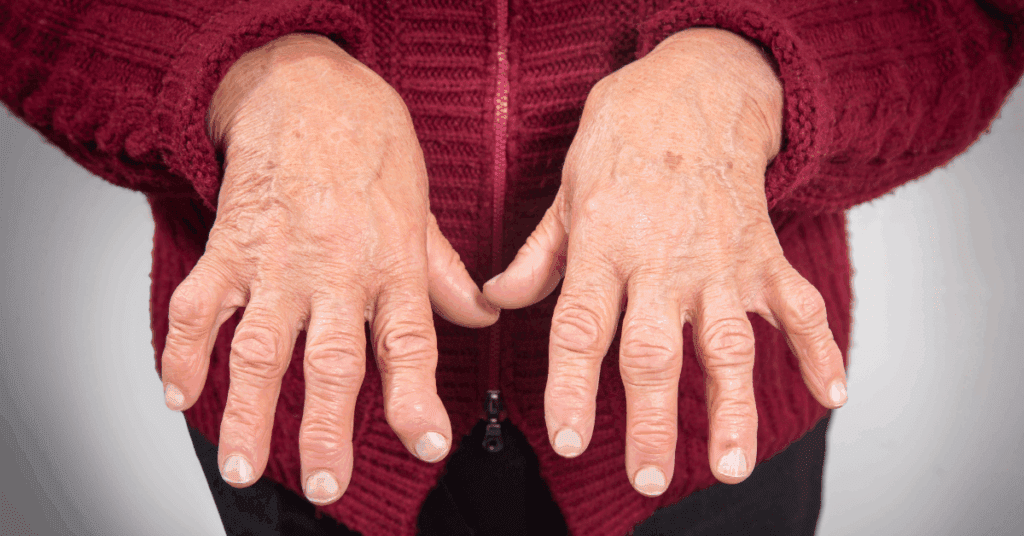
What does joint deformity mean?
A joint is where two bones meet and where movement can occur. Examples of joints include the knees, shoulders, hips, fingers, elbows, and toes. A joint deformity occurs when a joint becomes bent out of shape. This can happen to any joint of the body.
What causes deformity?
Common causes of acquired deformities include misaligned broken bones, osteoarthritis (a disease that causes the joints to degenerate), rheumatoid arthritis, and conditions like cancer and thyroid disease that cause tumours, goitres, or other masses to form. Some acquired deformities may be visible, but many are not.
How can deformity be corrected without surgery?
Non-surgical goals include pain relief and improved mobility and joint function through options such as Ayurveda and physical therapy.
Is deformity permanent?
The deformity may become worse over time if not treated. If the deformed position is not treated, it can result in stiffness. This can become permanent if you do not seek treatment.
REFERENCES
Patel, V et al. (2025). A rare case of triple deformity of knee secondary to Garre’s osteomyelitis. Multidisciplinary Science Journal.

Ashour, R, Jankovic, J. (2006). Joint and skeletal deformities in Parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Movement Disorders, 21.

Williams, D A et al. (2004). Knee pain and radiographic osteoarthritis interact in the prediction of levels of self-reported disability. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 51(4), 558–561.

Mishra, D S et al. (2025). FROM NIDANA TO CHIKITSA: Understanding Amavata Through the Lens of Ayurveda and Rheumatology. EPRA International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IJMR).