Results for {phrase} ({results_count} of {results_count_total})
Displaying {results_count} results of {results_count_total}
Popular Searches: DiseasesTreatmentsDoctorsHospitalsWhole person careRefer a patientInsurance
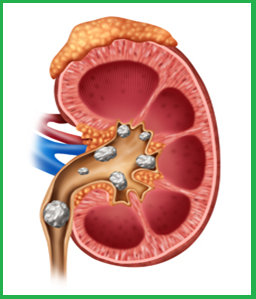
Kidney stones are hard, pebble-like pieces of material that form in one or both of your kidney when high levels of certain minerals are in your urine. Kidney stones rarely cause permanent damage if treated by a health care professional.
Kidney stones vary in size and shape. They may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a pea. Rarely, some kidney stones are as big as golf balls.
Kidney stones may be smooth or jagged and are usually yellow or brown. A small kidney stone may pass through your urinary tract on its own, causing little or no pain. A larger kidney stone may get stuck along the way. A kidney stone that gets stuck can block your flow of urine, causing severe pain or bleeding.
Do kidney stones have another name?
The scientific name for a kidney stone is renal calculus or nephrolith. You may hear health care professionals call this condition nephrolithiasis, urolithiasis, or urinary stones.
You probably have one of four main types of kidney stones. Treatment for kidney stones usually depends on their size, location, and what they are made of.
Calcium stones
Calcium stones, including calcium oxalate stones and calcium phosphate stones, are the most common types of kidney stones. Calcium oxalate stones are more common than calcium phosphate stones.
Calcium from food does not increase your chance of having calcium oxalate stones. Normally, extra calcium that isn’t used by your bones and muscles goes to your kidneys and is flushed out with urine. When this doesn’t happen, the calcium stays in the kidneys and joins with other waste products to form a kidney stone.
Uric acid stones
A uric acid stone may form when your urine contains too much acid. Eating a lot of fish, shellfish, and meat—especially organ meat—may increase uric acid in urine.
Struvite stones
Struvite stones may form after you have a UTI. They can develop suddenly and become large quickly.
Cystine stones
Cystine stones result from a disorder called Cystinuria that is passed down through families. Cystinuria causes the amino acid cystine to leak through your kidneys and into the urine.
Complications of kidney stones are rare if you seek treatment from a health care professional before problems occur.
If kidney stones are not treated, they can cause:
You are more likely to develop kidney stones if you have certain conditions, including
Urolithiasis is the stone formed in urinary tract (kidney, ureter, bladder, and urethra). Synonym for Urolithiasis is urine stone/calculi. In Ayurveda, it is known as Ashmari which means calculi or stone and its small powder like pieces are known as Sharkara or Sikatai.e. gravels. Classical Ayurveda explains two process of stone formation. One is by the stagnation and super saturation of the urine and other by crystallization of the crystalloids in the urine.
Various herbal formulations are mentioned in classical texts and are found effective till today. Specific group of drugs are mentioned on basis of type of stone on its Doshas combinations. Urine stones are classified on basis of doshas – Vata, Pitta, Kapha etc and treatment is mentioned accordingly. The drugs like Varuna, Pashanabheda, Trinapanchamoola, Gokshura, Punarnava, Apamargakshar, Chandraprabhavati etc. are advised to be administered either in form of decoctions, fermented solutions, powder, cold infusions etc or in form of dietary products like cooked rice, gruel etc. Stones which are too large and not responding to medicinal treatment should be extracted surgically and for this Sushruta, the text book of Ayurveda Surgery had mentioned perineal approach to remove the stone.
Ayurveda understands the imbalances of Doshas, primarily: Kapha Pitta and Vata to an extent, in presence of an imbalanced agni will vitiate the dhatus/tissue and lead to Granthi/Cystic formation.
*Outcome may vary from patient to patient
Bengaluru – Domlur Bengaluru – Aster CMI, Hebbal Bengaluru – HRBR Layout Bengaluru – Sri Shankara, Basavangudi Bengaluru – Bannerghatta Road Bengaluru – ArekereDelhi – New DelhiKochi – Kadavanthara Uttarakhand-Kalmatia, AlmoraChennai – Greams Road Chennai – Vanagaram Chennai – Kotturpuram Hyderabad – Somajiguda
Ayurveda Parasurgery Autoimmune Disorders Blood Disorders Cardiology Dermatology Endocrinology Ear-Nose Throat-Mouth Elder-Care Gastrointestinal Gynaecology Integrative Oncology Infectious-Diseases Liver-Hepato-Biliary-Care Mental Health and De-addiction Male-Reproductive-Disorders Nephrology Neurological-Disorders Orthopaedic Disorders Ophthalmology Obstetrics-Integrative Preventive-Health-Wellbeing Pulmonology Pediatric-Development-Disorder Sleep-Disorders
Any use of this site constitutes your agreement to the Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cancellation and Refund Policy
©2025 Apollo AyurVAID Hospitals. All rights reserved.
Popular Searches: DiseasesTreatmentsDoctorsHospitalsWhole person careRefer a patientInsurance